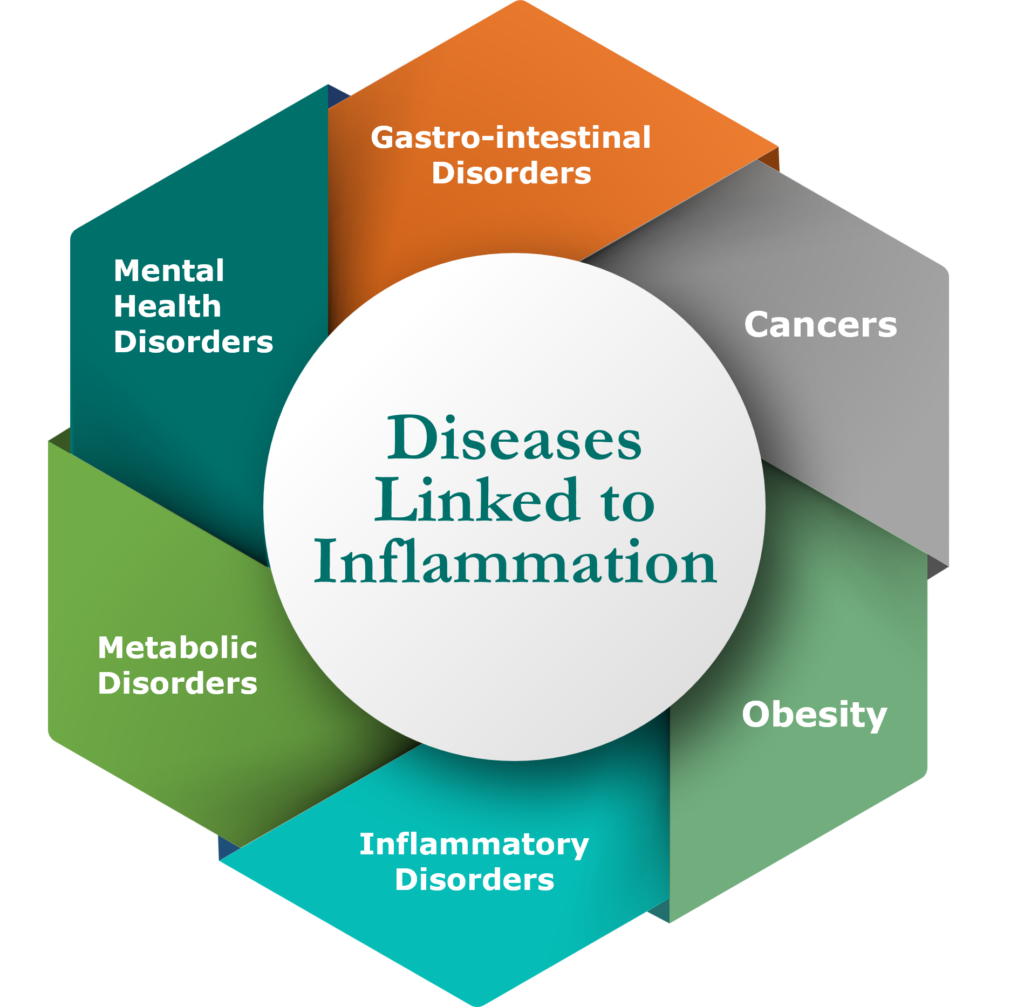
The Core of Neurodegeneration
GoodCap is dedicated to pioneering innovative therapeutic formulations for the treatment of psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders. Our strategies are centered on addressing the fundamental pathological mechanisms that underlie these conditions, which encompass the intracellular accumulation of neurotoxic substances and the consequent persistent neuroinflammation. These processes can not only trigger but also fuel progressive neurodegeneration.
By prioritizing these foundational mechanisms, GoodCap’s therapeutic candidates aim to disrupt the harmful cycle of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration that drives disease progression. Through this approach, our therapeutic candidates hold promise for broad applications spanning a wide spectrum of neuroinflammation-based psychiatric and degenerative disorders.
Chronic Neuroinflammation
Chronic neuroinflammation triggers increases in pro-inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species, which can lead to a variety of psychiatric disorders and neurogenerative diseases
GCAP001: GoodCap’s Unique Approach
Polymodal Activity
Targeting multiple clinically important biological pathways to downregulate IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, COX-2, and ROS

Known Biological Activity & Safety Profile
Utilize molecules that have known mechanisms and have established and attractive safety profiles.

Expediting Route to Clinic
Leveraging the safety profile of the formulation components to move into human trials quicker than NCEs

IP: Seeking CoM Coverage
Novel combination of molecule classes allows GoodCap to apply for composition of matter (CoM) coverage in the U.S. and internationally
Enhanced activity of GCAP001 on Inflammation
GoodCap’s lead therapeutic candidate is shown to significantly downregulate key pro-inflammatory cytokines
Redefining PTSD Therapy for the Future
Leveraging the profound insights from a decade of dedicated research and interaction with military veterans, GoodCap has identified critical gaps in mental health treatments, particularly for conditions like PTSD, depression, and anxiety. Inspired by this need for a more effective and comprehensive approach, we are on the forefront of developing advanced therapeutic formulations.
Our focus remains steadfast on transcending traditional treatment methodologies to deliver a novel drug product. With every advancement, GoodCap reinforces its commitment to transforming the landscape of treatment by pioneering deeper understanding and more effective combat against neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative disorders.
GoodCap’s co-founders have observed the significant impact of their drug prototypes, demonstrating remarkable outcomes in veterans afflicted with PTSD. This success has steered GoodCap’s commitment to empowering these individuals to reclaim their lives.
Abstract
Acute and chronic inflammation of the body triggers the production of pro- and anti-inflammatory pathways that can affect the content of cytokines in the brain and thus cause brain inflammation. Disorders such as depression and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) are often associated with elevated inflammation. Recently, positive and promising clinical results of psilocybin for the treatment of depression and PTSD were reported. Thus, we decided to test whether psilocybin alone or in combination with eugenol, an anti-inflammatory and antioxidant agent, would prevent the increase in or decrease the content of cytokines in the brain…
This demonstrates the anti-inflammatory effects of a combination of psilocybin and eugenol in the brain of animals with systemically induced inflammation.
Published in:
The leading international, peer-reviewed, open access journal of chemistry.
Molecules, March 2023, 28(6), 2624;
Abstract
Intestinal inflammation and dysbiosis can lead to inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) and systemic inflammation, affecting multiple organs. Developing novel anti-inflammatory therapeutics is crucial for preventing IBD progression. Serotonin receptor type 2A (5-HT2A) ligands, including psilocybin (Psi), 4-Acetoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (4-AcO-DMT), and ketanserin (Ket), along with transient receptor potential (TRP) channel ligands like capsaicin (Cap), curcumin (Cur), and eugenol (Eug), show promise as anti-inflammatory agents. […] This study is the first to explore the anti-inflammatory potential of psilocybin and 4-AcO-DMT in the intestines while highlighting the potential for synergy between the 5-HT2A and TRP channel ligands, specifically Psi and Eug, in alleviating the TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced inflammatory response in HSEIC. Further investigations should evaluate if the Psi and Eug combination has the therapeutic potential to treat IBD in vivo.
Published in:
An international, scientific, peer-reviewed, open access journal on molecular biology
Current Issues Molecular Biology, August 2023, 45 (8), 6743-6774.
Psilocybin and Eugenol Reduce Inflammation in Human 3D EpiIntestinal Tissue
Abstract
Inflammation plays a pivotal role in the development and progression of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), by contributing to tissue damage and exacerbating the immune response. The investigation of serotonin receptor 2A (5-HT2A) ligands and transient receptor potential (TRP) channel ligands is of significant interest due to their potential to modulate key inflammatory pathways, mitigate the pathological effects of inflammation, and offer new avenues for therapeutic interventions in IBD. This study investigates the anti-inflammatory effects of 5-HT2A ligands, including psilocybin, 4-AcO-DMT, and ketanserin, in combination with TRP channel ligands, including capsaicin, curcumin, and eugenol, on the inflammatory response induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and interferon (IFN)-γ in human 3D EpiIntestinal tissue. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to assess the expression of pro-inflammatory markers TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6, IL-8, MCP-1, and GM-CSF. Our results show that psilocybin, 4-AcO-DMT, and eugenol significantly reduce TNF-α and IFN-γ levels, while capsaicin and curcumin decrease these markers to a lesser extent. Psilocybin effectively lowers IL-6 and IL-8 levels, but curcumin, capsaicin, and 4-AcO-DMT have limited effects on these markers. In addition, psilocybin can significantly decrease MCP-1 and GM-CSF levels. While ketanserin lowers IL-6 and GM-CSF levels, there are no effects seen on TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-8, or MCP-1. Although synergistic effects between 5-HT2A and TRP channel ligands are minimal in this study, the results provide further evidence of the anti-inflammatory effects of psilocybin and eugenol. Further research is needed to understand the mechanisms of action and the feasibility of using these compounds as anti-inflammatory therapies for conditions like IBD.
Published in:
Life 2023, 13(12), 2345
Psilocybin and eugenol prevent DSS-induced neuroinflammation in mice
Abstract
Neuroinflammation has emerged as a central pathology common to several acute and chronic brain diseases. Recent studies have displayed the anti-inflammatory properties of naturally occurring compounds derived from mushrooms and plants could potentially reduce neuroinflammation and disease progression. In this study, we aimed to investigate the impact of psilocybin and eugenol, as well as their combinations, on neuroinflammation. To induce inflammation through the gut-brain axis, we employed a colitis mouse model via oral feeding of dextran sulfate sodium (DSS). By administering various concentrations and combinations of treatments, both before and after inducing inflammation, we sought to assess the synergistic anti-inflammatory effects of psilocybin and eugenol. Our findings revealed oral psilocybin and eugenol post-treatment significantly reduced the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and inflammatory mediators in the brain, including IL-1β, IL-6, and COX-2. Notably, combined treatment of psilocybin and eugenol exhibited the strongest reduction in IL-6 levels when compared to the DSS group. While both psilocybin and eugenol possess anti-inflammatory effects, the combined treatment overall did not demonstrate synergistic reductions in neuroinflammation across all markers. This study
adds to the growing body of evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of psilocybin and
eugenol in psychiatric and neurodegenerative inflammatory disorders. Further research is necessary to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of their anti-inflammatory effects and to evaluate their efficacy in clinical settings.
Published in:
Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 2024, 56, February 2024, 103033
Intellectual Property
Patent Application
“Compositions for Reducing Inflammation to Improve or Maintain Mental or Physical Health”
Claims capture both composition of matter and methods of use
Captures classes of molecules (TRP receptor agonists and 5HT2a receptor agonists) in various combinations including those in GCAP001
Provides wide range of pipeline opportunities via formulation modifications to target additional inflammation-based disease states including mood disorders, pain, digestive problems, substance abuse and cancer
Priority Date: October 11, 2020